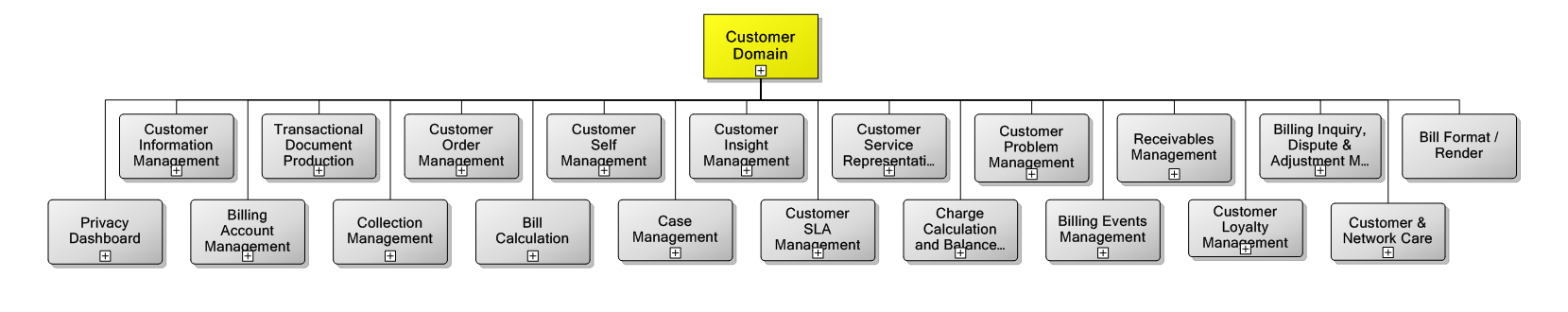
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) processes and functions are defined by the Business Process Framework (TMF GB 921) as the process grouping that considers the fundamental knowledge of customers needs and includes all functionalities necessary for the acquisition, enhancement and retention of a relationship with a customer.
The customer as defined by the e-TOM e-business reference model is responsible for ordering, using and (usually) paying for service products. The customer may represent an end-customer, where the product provided by the value network is consumed, or a wholesale customer that resells the product provided, generally with some added value. The customer may also be a corporate customer that potentially has many contact people, departments, sites, services and billing accounts with the service provider.
CRM encompasses the end to end lifecycle of the customer, from customer initiation/acquisition, sales, ordering and service activation, customer care and support, proactive campaigns, cross sell/up sell and retention/loyalty. CRM needs to involve all the touch points and channels to the customer, including contact center, retail stores, dealers, self service, and field service, as well as via any media (phone, face to face, web, mobile device, Chat, Email, SMS, mail, the customerís bill, etc.).
As an example, the following diagram describes the typical work flow of customer service representatives (CSRs) of Communication Service Providers (Diagram Figure 7: Typical work flow of Customer Service Representatives).
Another significant component of CRM evolves around marketing activities. This includes retention management, cross-selling, up-selling and direct marketing for the purpose of selling to customers. CRM also includes the collection of customer information and its application to personalize, customize and integrate delivery of service to a customer, as well as to identify opportunities for increasing the value of the customer to the enterprise.
In the Telecom Applications Map, a number of systems and applications provide these functions. Typically an operator may have the following applications:
This was created from the Frameworx 16.0 Model